What Is a CCMS and Why Your Organization Needs One: A Guide for IT and Access Managers

Managing credentials, access rights, and digital identities can quickly become chaotic in any organization. Suppose you’re responsible for IT, security, or operations. In that case, you may have already noticed gaps in how badges, digital certificates, and mobile credentials are issued and tracked. That’s where a CCMS comes in.
We’ll explain what a CCMS is, why it matters, how it works, and how to choose the right one for your organization—without getting lost in jargon.
What is a CCMS?
CCMS stands for Credentials or Certificates Management System (sometimes called “Credentials Control Management System”).
In simple terms, a CCMS is a central system that lets you:
- Issue credentials (physical cards, digital certificates, mobile credentials)
- Manage and monitor them throughout their lifecycle
- Tie credentials to access rights and identity
- Revoke or suspend credentials if needed
Examples of credentials a CCMS might manage:
| Credential Type | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|
| Smart cards | Building access or secure workstations |
| Digital certificates | Authentication, encryption, digital signatures |
| Mobile credentials | Phone-based access to doors, apps, or systems |
| Biometric/FIDO devices | Strong authentication for high-security systems |
Think of a CCMS as your control centre for identity and access—it answers the questions: “Who has what credential? What access do they have? When does it expire?”
Why Your Organization Needs a CCMS

Even if your organization has a few badge systems or certificate tools, a CCMS adds value in ways that siloed systems cannot. Here’s why:
1. Unified Management of Identity & Access
Without a CCMS, badge systems, certificate servers, and mobile credentials all operate separately. A CCMS brings them together, letting you manage:
- Issuance
- Revocation
- Lifecycle tracking
This means no more juggling spreadsheets, manual logs, or separate systems.
2. Improved Security & Reduced Risk
A CCMS reduces the chance of human error or unauthorized access. Features like automatic certificate renewal, revocation tracking, and status monitoring make it easier to:
- Prevent compromised credentials from being used
- Avoid service downtime due to expired certificates
- Ensure access rights are always up to date
3. Support for Digital Signatures and PKI Workflows
Digital signatures rely on certificates. A CCMS handles:
- Issuing digital certificates
- Embedding them in smart cards or mobile credentials
- Automatically renewing certificates
- Managing who can sign and under what conditions
This establishes a secure and auditable workflow for contracts, approvals, and agreements, ensuring transparency and accountability.
4. Scalability and Future-Proofing
Manual or siloed systems don’t scale well. A CCMS can handle:
- Thousands of users and devices
- Multiple credential types
- Regional or departmental authority separation
This prepares your organization for mobile credentials, biometric authentication, and other emerging technologies.
5. Audit, Compliance, and Lifecycle Control
A CCMS makes reporting and compliance easier:
- Logs of issued, revoked, and expired credentials
- Tracking of active users and failed access attempts
- Support for regulatory audits and internal security policies
How a CCMS Works: Credential Lifecycle
Here’s a simplified view of the CCMS process:
- Enrollment/Provisioning
- Users or devices are registered
- Credentials are tied to identities
- Integration with HR or directory services
- Issuance
- A physical or digital credential is delivered
- Could be a smart card, mobile token, or certificate
- Lifecycle Management
- Credentials are monitored for expiration
- Automatic renewal or revocation when needed
- Access Control / Authentication
- A credential is used for physical or logical access
- CCMS ensures validity and correct access rights
- Revocation / End-of-Life
- Compromised or retired credentials are deactivated
- Reporting / Monitoring
- Dashboards show usage, blocked credentials, and failed logins
With this lifecycle, organizations gain complete oversight of identity and access, reducing risk and operational headaches.
Key Features to Look for in a CCMS
When evaluating solutions, focus on these essential features:
- Support for multiple credential types
- Smart cards, badges, mobile, biometric/FIDO devices
- Integration with existing systems
- Active Directory/LDAP, HR systems, access control, signature servers
- Lifecycle management & automation
- Automatic certificate renewal, alerts, and revocation
- Scalability and modularity
- Handle large volumes of users/devices
- Support central or decentralized deployment
- Strong security architecture
- PKI, RSA/ECC keys, audit logs, separation of duties
- User-friendly interface
- Admin dashboards and user self-service
- Reporting & analytics
- Credential usage, failed attempts, and trends
- Compliance and audit capabilities
- Full tracking for regulatory requirements
- Operational efficiency
- Reduce manual work, errors, and downtime
CCMS and Digital Signatures
Digital signing workflows (contracts, approvals, internal sign-offs) depend on strong identity verification. Without a CCMS:
- Certificates may expire unnoticed
- Identity verification may be inconsistent
- Signatures may not be auditable
A CCMS ensures:
- Certificates are issued and embedded in devices
- Automatic renewal avoids workflow interruptions
- Access rights for signing are controlled
- All activity is tracked and auditable
In short, if your organization uses digital signature for your organization, a CCMS is essential.
Real Tip
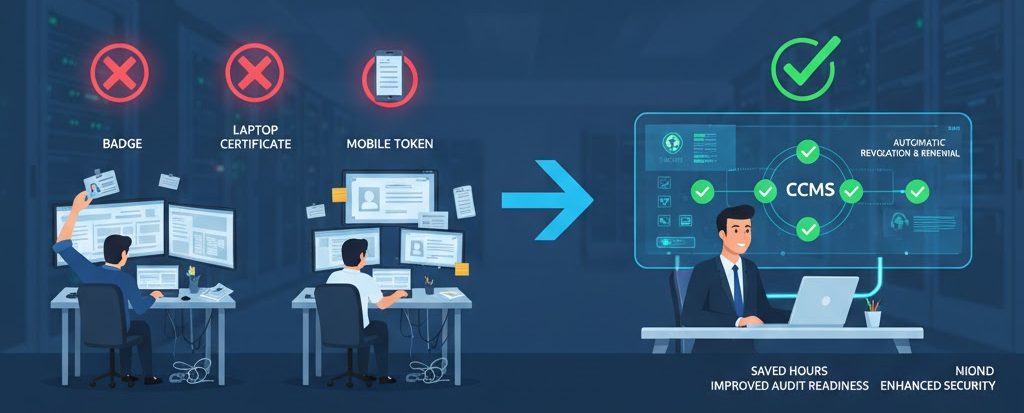
In one mid-sized enterprise I worked with, employees had badges, laptop certificates, and mobile tokens, all of which were managed separately. When a contractor left, we had to manually revoke three different credentials across multiple systems, which caused delays and a security risk. After implementing a CCMS, revocations and renewals became automatic. It saved the IT team hours every month and significantly improved audit readiness.
FAQs
Do we really need a CCMS if we already have badge and certificate systems in place?
Yes. Point systems often operate in silos. A CCMS unifies credential management, reduces gaps, and improves auditability.
How do we justify the investment to management?
Focus on:
- Risk reduction (credential misuse, identity theft)
- Operational efficiency (automation, fewer errors)
- Compliance (audit-ready reporting)
- Future flexibility (mobile credentials, digital signatures)
What if we only need badges and door access?
Even simple systems grow over time. Mobile credentials, digital signatures, and cloud integration will likely become necessary. Starting with a CCMS avoids the need for complicated retrofitting later.
Final Thoughts
Adopting a CCMS is more than buying a credential management tool—it’s building a secure, scalable identity infrastructure.
The benefits are clear:
- Unified control of credentials
- Reduced risk and human error
- Support for digital signatures and modern authentication
- Full auditability and compliance readiness
For any organisation with identity, access, or signing needs—whether large or growing—a CCMS is a strategic investment, not just an operational tool.
