Engineering Magic Behind Games That Handle Millions of Players at Once

It now seems perfectly normal to log into your favorite multiplayer game and see thousands of other players running around. However, most gamers are unaware of the extremely intricate technical infrastructure that underlies that flawless experience. It takes engineering solutions that push the limits of modern computing to support millions of concurrent connections.
You gain a fresh perspective on the games you play on a daily basis when you comprehend how these systems operate. It also clarifies why some games manage crowds better than others and why server problems occur during significant launches.
Distributed Server Architecture
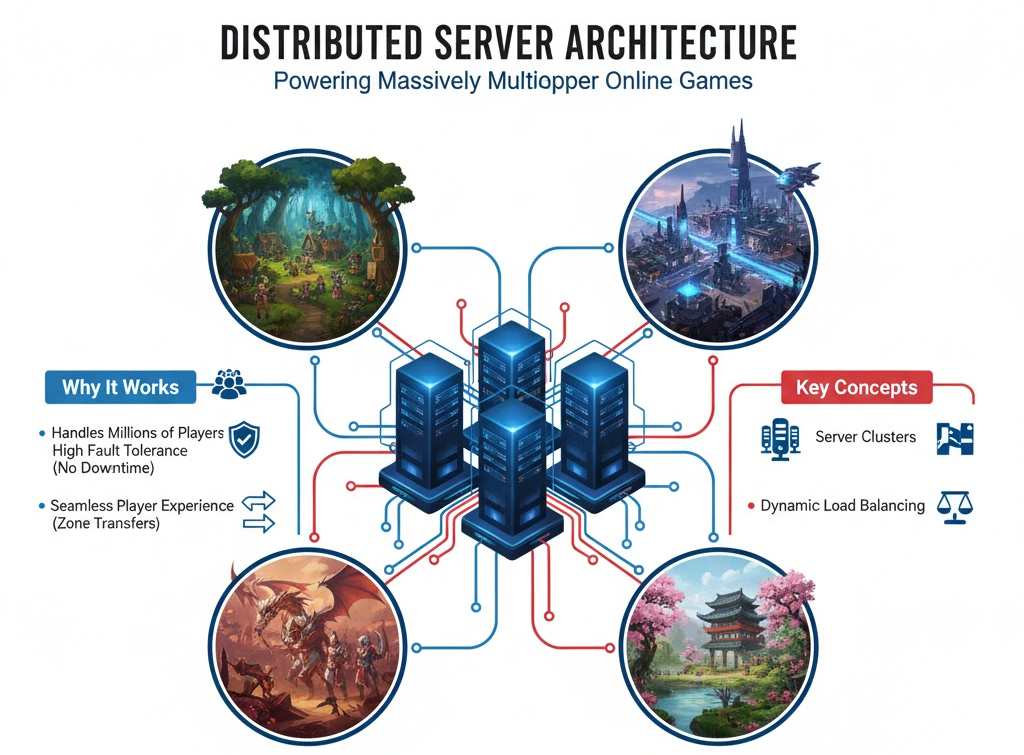
Millions of players cannot be handled by a single computer. Modern games, on the other hand, distribute the workload among hundreds or thousands of cooperating servers. Because of this distributed approach, players won’t notice any issues when one server fails or becomes overloaded.
The game world is frequently split up into instances or zones, each of which is run by clusters of dedicated servers. Your connection transfers between servers with ease as you move from one location to another. Over decades, games like World of Warcraft and Final Fantasy XIV have improved this technology, enabling the simultaneous operation of entire virtual continents.
Load Balancing and Player Distribution
Players are directed to the servers that are most capable of handling them by intelligent routing systems. When you log into popular online games, algorithms determine the best connection point based on your location, server loads, and network conditions. Before you even see the character selection screen, this occurs in milliseconds.
These systems become even more important during peak hours. Ten times as many players may attempt to connect at once when a new expansion launches. In order to distribute this traffic among the available resources, load balancers spin up extra server instances during periods of high demand and scale back down during times of low demand.
This procedure has been completely transformed by cloud computing. Instead of keeping pricey hardware that is idle most of the time, developers can rent server capacity on demand with services like Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud Platform.
Database Management at Scale
In a multiplayer game, every move you make must be captured somewhere. Databases that must manage millions of read and write operations per second house your inventory, accomplishments, quest progress, and social connections. This pressure would cause traditional database systems to crumble.
Specialized database solutions created for precisely this problem are used in modern games. Some use a method known as sharding to distribute data among several database servers. Others use in-memory caching systems to store frequently accessed data so it can be quickly retrieved. In reality, your character data may exist in multiple locations at the same time, with advanced synchronization guaranteeing consistency.
The stakes are very high. A database failure could result in thousands of players losing progress, transforming a small technical problem into a PR nightmare.
Network Optimization and Latency Reduction
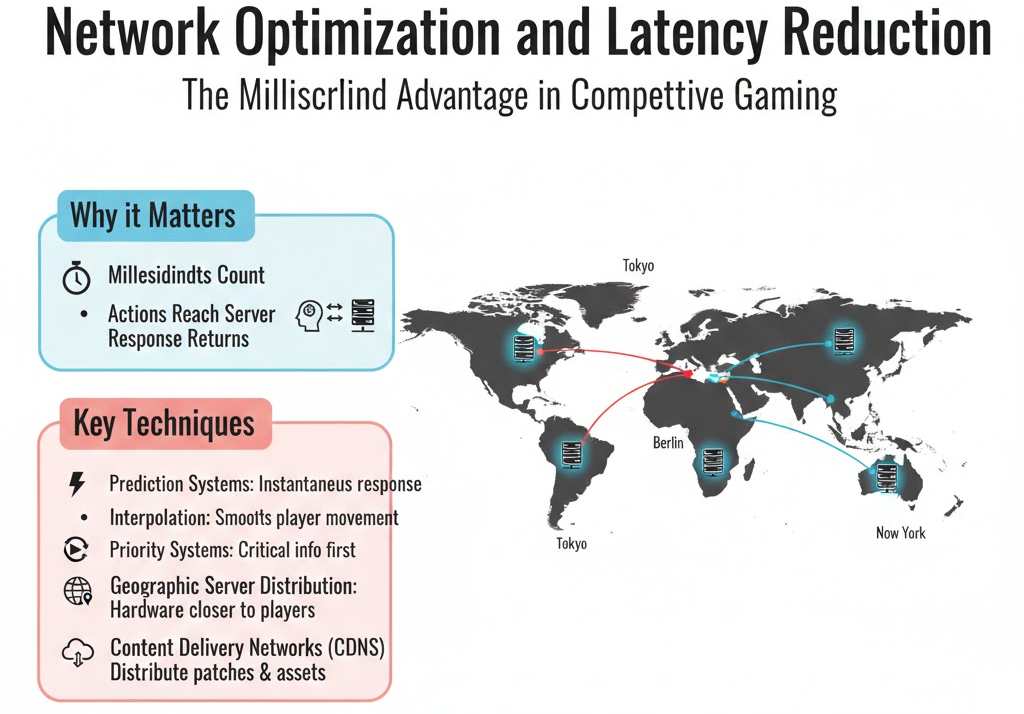
In competitive gaming, milliseconds count. Whether your shots land or your abilities activate at the appropriate time depends on how long it takes for your actions to reach the server and for the response to return. To reduce this delay, developers use a variety of strategies.
Prediction systems give the impression of instantaneous response by allowing your client to display actions before the server verifies them. Interpolation smooths out other players’ movements between network updates. Priority systems make sure that critical game information gets to you faster than secondary information like chat messages or visual effects.
Hardware is positioned closer to player populations through geographic server distribution. While someone in Berlin routes through European data centers, a gamer in Tokyo connects to servers in Asia. Originally designed to stream video, content delivery networks now aid in the worldwide distribution of game patches and assets.
Real-Time Communication Systems
In multiplayer games, players need to be able to see each other’s movements almost instantly. For this, communication protocols that put speed ahead of reliability are required. Unlike loading a webpage, where every piece of data must arrive correctly, games can tolerate occasional packet loss if it results in faster overall performance.
Voice chat adds yet another level of complexity. To process audio from dozens of players at once with minimal latency, specialized systems must work in tandem with the main game servers. While some games use specialized services, others develop their own proprietary solutions.
Platforms that have features like a tiktok story viewer, where millions of users concurrently access and interact with constantly updated content, face a similar issue.
Why This Matters for Players
All of this invisible infrastructure directly affects your gaming experience. Strong technical foundations make games feel responsive and dependable. Poorly designed backends cause rubberbanding, disconnections, and frustrating lag spikes that ruin otherwise excellent gameplay.
Keep in mind that a great deal of engineering work made it possible for you to enjoy a seamless session with thousands of other players. The next time a launch day goes awry, you’ll see how difficult their work is.One of the most difficult real-time computing problems that exists today is multiplayer gaming. The fact that it typically functions so well is evidence of how far technology has advanced.
